Allocation Unit - The Building Block of Data Storage
Have you ever wondered what the “Allocation Unit Size” option means when formatting a drive? Whether you’re setting up an SSD, HDD, or USB, this tiny detail can have a significant impact on how your storage performs. If you’ve been confused by this term, you’re in the right place!

Many people overlook allocation units during formatting, thinking they don’t matter, but in reality, the choice can affect everything from storage efficiency to read/write speed.Understanding how these units work can help you make smarter choices when managing your drives. Tools like GUI Format make this process simple by allowing you to adjust allocation settings for optimal performance.In this article, we’ll break down everything you need to know about allocation units, how they work, why they matter, and how to choose the best size for your storage needs.
What Is an Allocation Unit?
The smallest piece of storage space used by a file system to hold data is called an allocation unit, sometimes referred to as a cluster. The system allots one or more of these units to store data when you save a file.For instance, if your disk has a 4 KB allocation unit size, then every file, regardless of its size, will occupy at least 4 KB.The operating system can rapidly and effectively handle and locate files because of this structure. Your drive's performance and capacity utilization are impacted by the size of each allocation unit, which dictates how data is stored and retrieved.To put it simply, allocation units are little "containers" that hold your data; selecting the appropriate container size guarantees optimal drive performance.
Why Allocation Units Matter?
Allocation units determine how efficiently your drive uses its storage space. Choosing the right size can significantly impact:- Storage Efficiency: Smaller allocation units reduce wasted space (also known as slack space) but can slightly slow down read/write performance.- Performance: Larger units improve speed for larger files, such as videos or games, since fewer clusters need to be read or written.- File System Health: Properly aligned allocation units reduce fragmentation and help maintain drive performance over time.- Drive Lifespan: Optimal allocation sizes help prolong the life of your storage device by reducing unnecessary write cycles, particularly on SSDs.
Choosing the Right Allocation Unit Size
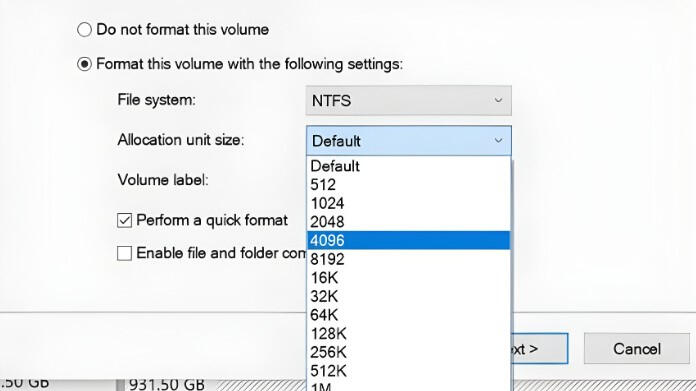
The type of data you keep and how you intend to use your disk will determine the best allocation unit size. While the incorrect size can slow your system or fill your drive more quickly, the right size can improve performance and reduce wasted space.Here are some simple guidelines:- 4 KB: Ideal for everyday use with small files like documents or images.- 16 KB to 64 KB: Great for large files such as videos, games, or databases.- 128 KB or more: Best for backup or storage drives with huge files.You can choose the allocation size that best suits your needs while formatting your drive using programs like GUI Format. Making informed decisions guarantees that your drive will continue to be quick, effective, and long-lasting.
Allocation Units and File Systems
Performance, compatibility, & storage efficiency are all impacted by how various file systems handle allocation units.1. FAT32: Frequently utilized on USB devices, it has a 4 GB file size limit but allows for customizable allocation amounts.2. NTFS: The Windows standard contains features like compression & permissions, and effectively manages both tiny and large files.3. exFAT: It is compatible with many operating systems, supports huge files, and is perfect for flash devices.Selecting the appropriate file system & allocation unit size guarantees that your drive operates effectively, remains compatible, and functions flawlessly on many devices.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
1. Using the Wrong Allocation Size: For tiny files, setting a unit too ample wastes space; for large files, setting a size too small slows down performance.2. Skipping Format Tools: Using the built-in format options does not always provide complete control over formatting. When configuring disks, tools like GUI Format offer you dependability and versatility.3. Ignoring File System Type: Performance can be lowered and allocation unit customisation limited by selecting the incorrect file system.4. Not Backing Up Before Formatting: Before changing allocation units, many users neglect to make a backup of crucial data. Always make a backup of your files before formatting because formatting removes all existing data.
Final Thoughts
Allocation units may seem like a minor detail, but they play a crucial role in how your drive stores and accesses data. By understanding and selecting the proper size, you can strike a balance between performance, efficiency, and longevity for your storage device.Whether you’re setting up a new SSD or reformatting an external drive, tools like GUI Format can make the process smoother and more customizable.Taking a few moments to understand allocation units can help you maximize your storage efficiency, with no wasted space and no unnecessary slowdowns.
About the Author:
I'm Wilford Conrad, a web developer, computer enthusiast, and gamer who likes to delve deeply into the workings of technology.To help people make more informed IT decisions, I write about data management, storage systems, and performance optimization.I would love to hear from you if this article was helpful or if you have any other opinions about allocation units. Let's continue the discussion!
Ref:
GMODISM. (2020, September 14). Allocation Unit size explained - What you should set the allocation unit size to when formatting [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2gI1yPYxWHE